- engitech@mail.com
- Mon - Sat: 8.00 am - 7.00 pm
We are creative, ambitious and ready for challenges! Hire Us
We are creative, ambitious and ready for challenges! Hire Us
MRP processes inside of ERP systems have many limitations which prevent accurate calculations of when and which materials need to be purchased.
Some examples of ERP limitations:
|
Manufacturing Requirement
|
ERP - MRP limitations
|
|---|---|
|
Long Production Orders (e.g. Multi-week Orders)
|
MRP engines typically require all materials to be available at the start of an order. For long-running orders this is unrealistic and materials are received at periodic intervals during the order run span.
|
|
Consider Production Capacity and alternative BOMs
|
MRP processes typically run assuming infinite capacity based on Just In Time Production. This results in material requirements identified too early or too late. Early is usually acceptable however if an order could be advanced to avoid a future capacity bottleneck then required materials may not be ordered in time. Another limitation in most ERP systems is the inability to handle situations such as machine specific or time effective BOMs
|
|
Material Expiration Transition Use up and Replace
|
ERP systems require explicit association of BOM versions to orders. In some cases a required material may expire mid-way through an order. Typical ERP? MRP engines cannot handle such situations and often require orders to be split and assigned different BOM versions. In reality it is hard to split an order around a specific calendar date as the order may slide forwards or backwards and in some cases there is not a hard date for transitioning from one material but there is a requirement to use up the expiring material before introducing the replacement material. Inaccurate handling of such scenarios can lead to costly expiration of otherwise usable materials.
|
|
Released Materials
|
Often an entire pallet of material may be issued against an order as the pallet is taken out on the shop floor against an order. In reality it may only be some portion of the material on the pallet that is required and the remaining is returned upon order completion. ERP systems can lose visibility of released materials and do not have a way to factor in materials that will be returned. This can result in more material ordered when not needed.
|
|
Support Scenario Analysis
|
E.G. for purchasing purposes it is useful to segregate materials required to cover committed or released production orders (required to supply open sales orders) and exclude materials required to cover planned orders (possibly based on forecast). Usually not practical to configure ERP? MRP engines to run MRP in different scenarios.
|
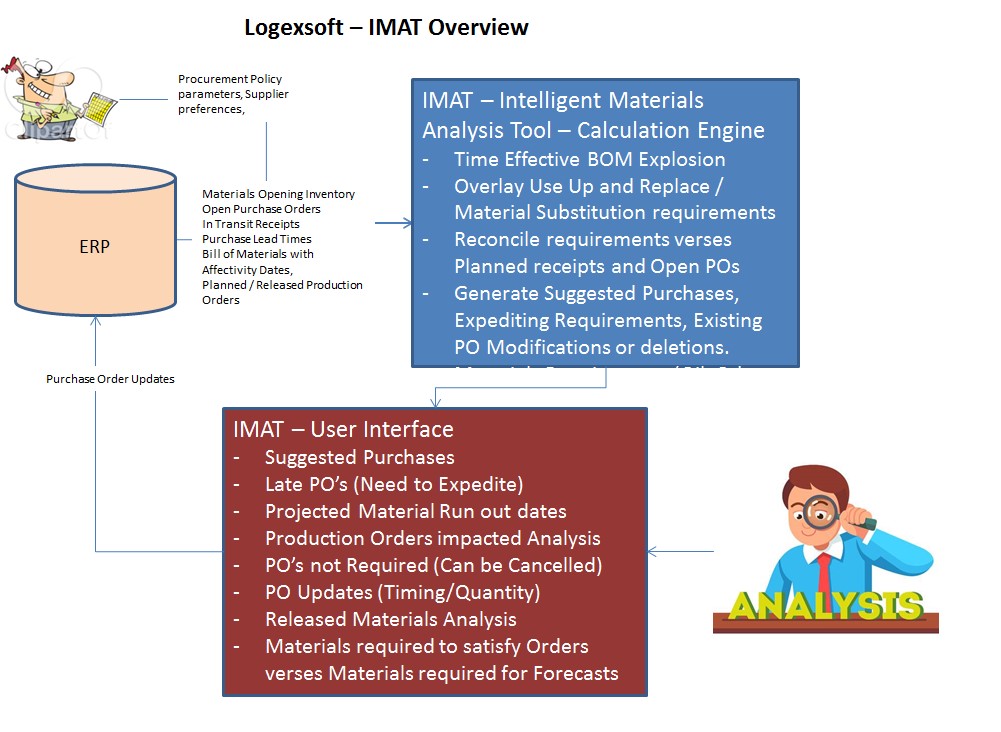
Ashlaketech has created the IMAT (Intelligent Materials Analysis Tool) using AspenTechTM SCM software.